Recycling renewables: Giving new life to wind, solar energy parts
(Prairie News Service) As Earth Month wraps up, more attention is being given to how to make use of wind and solar components at the end of their useful lives - and it includes emerging research in North Dakota.
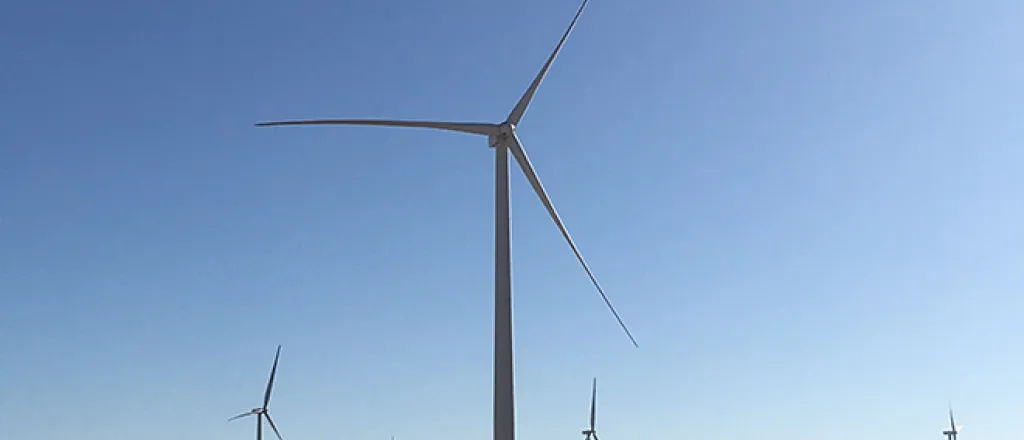
Wind turbines and solar farms are viewed as vital parts of the world's transition to renewable energy, but folks with North Dakota's Energy & Environmental Research Center have said the region will eventually have to make plans for more than 1,500 turbines using 4,500 blades, as these systems are upgraded or retired.
Josh Strege, the center's assistant director of energy systems, has been leading research into this area, and said these blades are made up of a lot of different materials.
"Our focus," he said, "has largely been on, 'Is there a way we can separate material A from material B?'"
His team suggested it would be more optimal to do that separation at the wind-turbine site, so large blades don't have to be transported and left to sit in a landfill. Strege said more research funding is needed to lay out an efficient process that would allow more of these blade parts to be reused, recycled or repurposed.
And it isn't just wind at the center of this movement. Karen Drozdiak, global director of ESG and sustainability at First Solar, the nation's largest solar panel maker, said her company has been at the leading edge of establishing a global recycling program within the industry.
"We focus not just on recovering the glass and frame materials, but we've also achieved closed-loop recovery of the semiconductor material in our solar panels," she said, "and that's being used to manufacture new solar panels."
Her company has its own in-house recycling facilities, but Drozdiak suggested broader investments within the sector are needed to keep more solar-panel materials in circulation after their first run. The International Renewable Energy Agency estimated that end-of-life solar panels could provide a recoverable value of $15 billion by 2050. Most wind and solar systems have a life span of about a quarter-century.