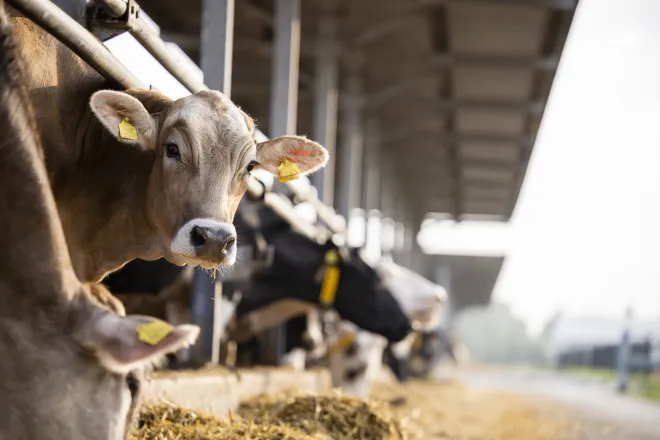
Nebraskans get advice on dealing with growing number of CAFOs
Click play to listen to this article.
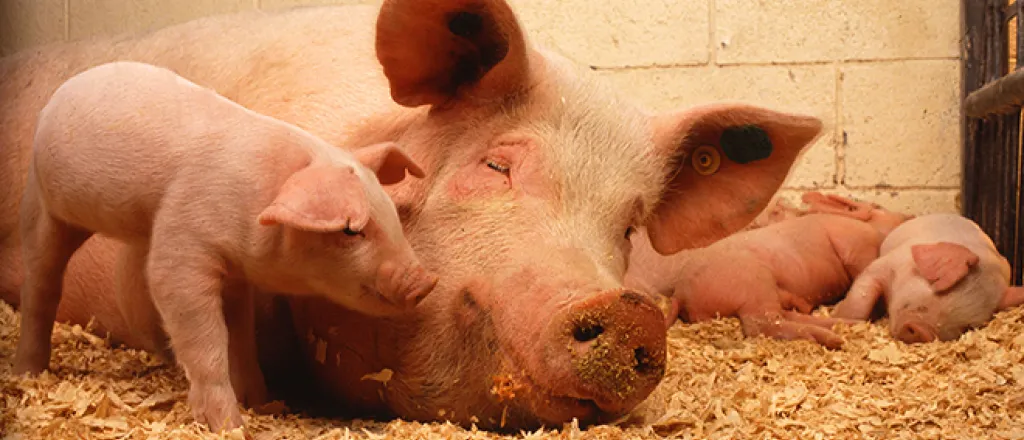
(Nebraska News Connection) Iowa has thousands fewer square miles than Nebraska but it has almost 3,000 more concentrated animal feeding operations, or CAFOs.
Opponents of the giant facilities argue there are enough. The increase in CAFOs nationwide has fueled opposition from nearby residents, along with environmental and animal rights groups.
In Iowa, one grassroots group has prevented around 100 of them from being built. Barb Kalbach, president of Iowa Citizens for Community Improvement, attributes Iowa's dismal water quality in large part to runoff from animal waste, applied to farm fields along with commercial fertilizer. Kalbach thinks rural Nebraska communities should also oppose such developments.
"That manure has to go somewhere," Kalbach pointed out. "It's not a question of, 'Well, should I, or I shouldn't I, put it on the ground,' you know? It's got to go. They've got to empty the pit, and so it's going to go. And if you have any kind of water issues whatsoever, people need to organize immediately."
The Environmental Protection Agency calls animal manure "a primary source of nitrogen and phosphorus to surface and groundwater." Roughly 20 percent of public water supplies and private wells in Nebraska test above recommended nitrate and nitrogen levels.
Jonathan Leo, a Nebraska environmental and land-use attorney, said CAFO owners usually contract with local farmers to use the animal waste. He noted for the largest operations, the massive amount of waste makes a methane digester system imperative.
"It breaks down manure into methane, which is a major greenhouse gas, for sale as an energy source to third parties," Leo explained. "And digestate, which is sold to off-site farmers as a nutrient additive to soil."
Leo and others helped residents of a small Nebraska town prevent development of a CAFO by an Iowa producer for more than 6,000 head of swine. Leo pointed out many who opposed it were farmers themselves.
"We worked with them about how to organize and understand their county's ordinance, with respect to CAFO permitting," Leo recounted. "And they appeared before their county board and their planning commission in a way that their own supervisors said, 'We've never seen this kind of citizen activism before.'"
The defeated operation would have been about a half-mile uphill from a stream which feeds a state recreation area lake used for swimming, boating and fishing.
As a result of a lawsuit by Food and Water Watch, the Environmental Protection Agency has agreed to begin studying the polluting effects of CAFOs, after years of being urged to do so.
















